Clean Technology Achieves Sustainability
30 August 2022How does Swirltex help municipalities while treating wastewater?
8 November 2022How can mining companies benefit from water reuse and cost savings using the Swirltex technology?
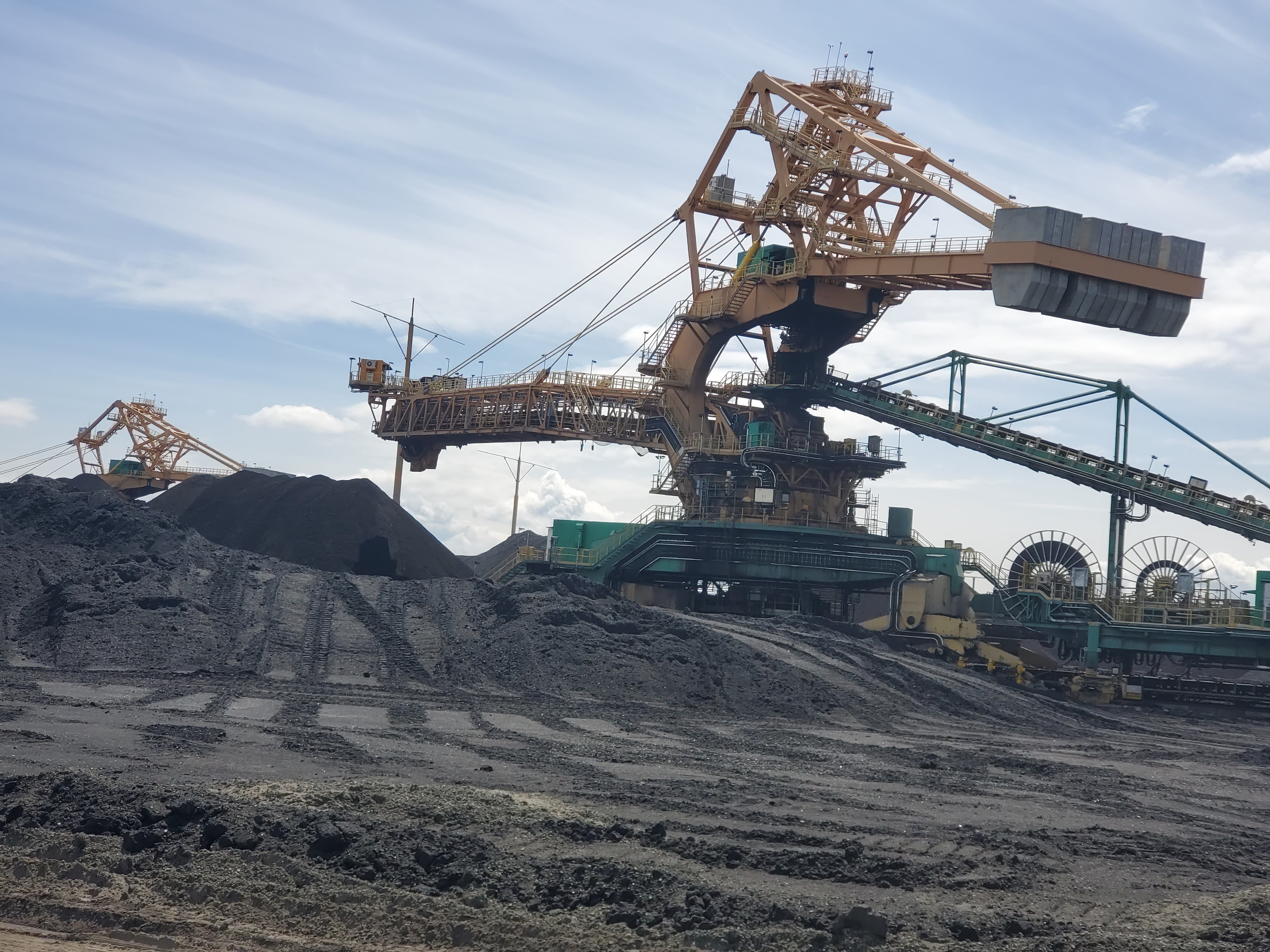
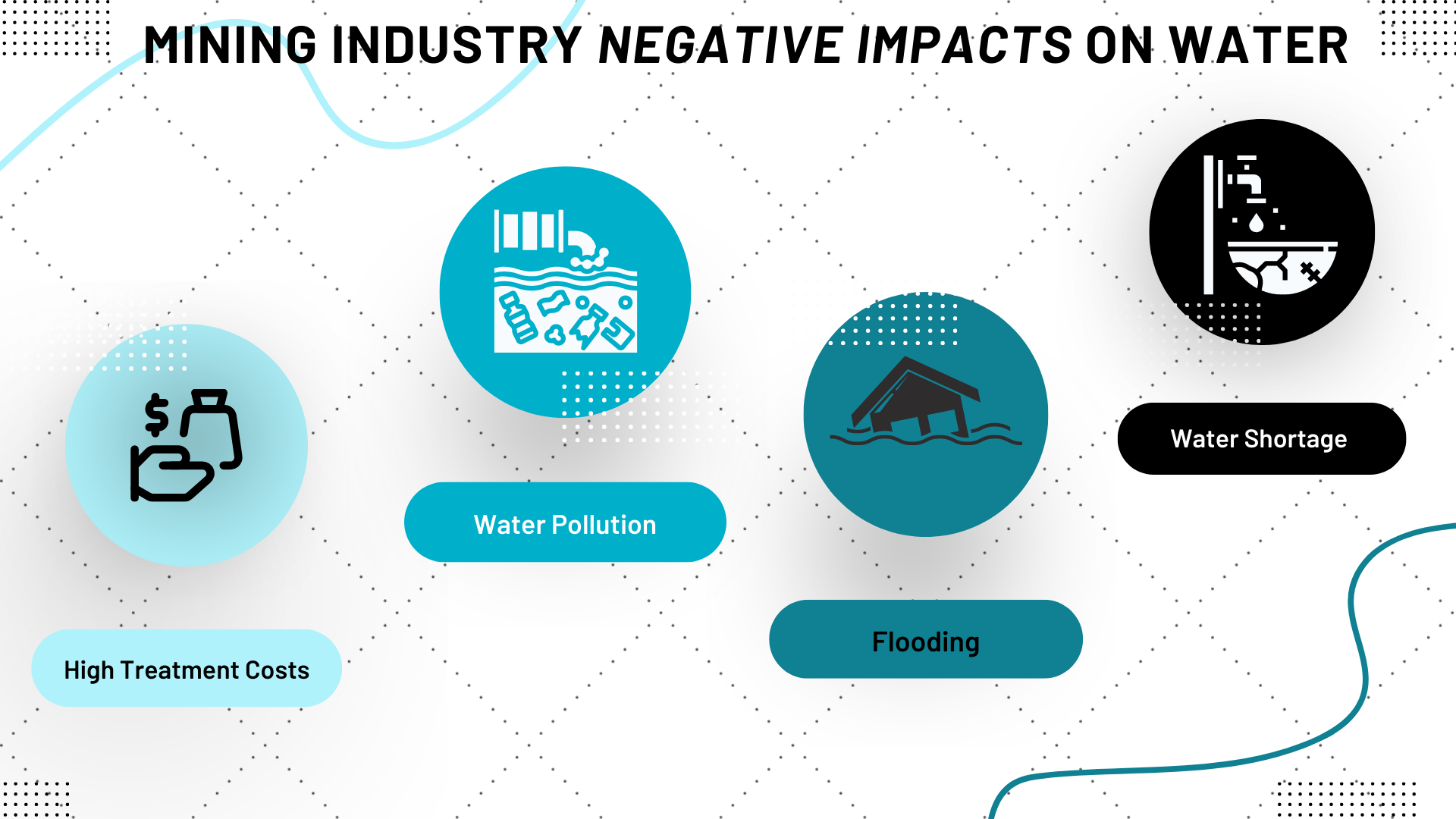
Water is a resource that is crucial to all kinds of mining operations. In this sector, precious metals are typically recovered from the ore using water. The mining industry has a major negative impact on water, caused by a variety of reasons. Either it is reducing the water supply or it is contaminating bodies of water with waste rock impoundment discharge. We all rely on water, yet there are growing hazards to it from human activities like mining for ore or heavy metals. Generally, mining wastewater contains high levels of acid contaminants and suspended solids. Wastewater generated by mining processes critically requires treatment as the influent include contaminants and other solids. As a result, polluted wastewater is not recycled or dumped back into the environment.
How much usage of water do mining companies have?
Public acceptance of mining requires global sustainability awareness and regulations that have fostered better water practices in the industry. There can be several mining wastewater treatment procedures, which often involve distinct stages and technologies. The price people pay for using these minerals every day can be extremely high. By its very nature, mining consumes, diverts, and potentially pollutes water resources.
Even though there have been improvements to mining practices lately, significant environmental risks still exist. One of the major problems is that, lately, more and more mining processes can be mechanized. Hence, it can lead to a significant increase in mining waste. According to 500 water scientists, people will be forced to live with severe water supply problems within the span of the next two generations if necessary actions to save water are not taken. Climate change and water pollution are the main factors in this water shortage in the future.
In most mining operations, water is sought from groundwater, streams, and ponds. Water is primarily used in mining for slurry transport, dust separation, and mineral processing. In most mining operations, water is sought from groundwater, streams, and ponds. However, mine sites are located in areas where water is already scarce, like local communities. Authorities from these local communities often don’t support the water usage done by these mines.
Why do these companies need to reuse water?
According to a survey done by CDP, 64% of businesses have experienced detrimental water effects in the past five years. The report also mentions that flooding, diminished water quality, and water shortages have major impacts caused by processes in this industry. Moreover, this leads to an increase in operating costs for more than half of the impacts mentioned above. The mine water is usually stored in above-ground dams or underground caverns. There is a necessity for mining wastewater treatment to ensure an environment with no pollution. Water pollution has become a key concern for global ecologists around the world. So, what should companies do to make water reusable?
How can Swirltex help in reusing water and cost savings?
Mining companies are looking into treating their wastewater. However, the treatment options available are costly. With Swirltex’s technology, complex waste streams can be treated while saving costs. Our system separates solid waste contaminants (TSS, TOC, Iron, and other contaminants) based on buoyancy while producing high-quality permeate for reuse. Even though the treatment is essential, having to spend such OPEX and CAPEX makes companies detour from this route.
At Swirltex, our clients save costs in several ways:
1. Our system’s minimal maintenance requirements.
2. A decrease in membrane fouling.
3. A fraction of the energy used by an average system.
We achieve where others fail in the most challenging applications. With systems that are effective, efficient, and created to consistently produce excellent outcomes, Swirltex is the filtration of the future.
Curious to know how efficient our technology is? Check out our Coal Case Study to see our results!